NTP Pool, a global network of time servers, plays a crucial role in keeping our digital world synchronized. Imagine a world where clocks on your devices are constantly out of sync, causing chaos in online transactions, communication, and critical systems. NTP Pool addresses this by providing a reliable and accessible source of accurate time information, ensuring that computers and devices around the globe operate seamlessly.
The NTP Pool Project, a volunteer-driven initiative, has established a vast network of servers across the internet, offering a free and readily available service for time synchronization. This project has significantly contributed to the stability and reliability of internet infrastructure, ensuring that time-sensitive applications function correctly.
What is NTP Pool?
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a crucial protocol that synchronizes the clocks of devices across a network. The NTP Pool Project is a volunteer-driven effort that provides a vast and reliable network of time servers, collectively known as the NTP Pool, to facilitate accurate time synchronization for internet users.
Purpose of NTP Pool
The NTP Pool serves as a centralized repository of time servers, offering a readily available source of accurate time for devices connected to the internet. This ensures that all devices on the network are synchronized to a common time standard, eliminating inconsistencies and potential issues arising from time discrepancies.
Role of the NTP Pool Project
The NTP Pool Project is a collaborative initiative where individuals and organizations volunteer their servers to contribute to the pool. The project’s primary role is to maintain and operate a robust network of time servers, ensuring that users have access to accurate and reliable time information. The project’s contribution to the internet is significant, as it enables consistent timekeeping across diverse networks and devices.
Benefits of using NTP Pool
- Improved Time Accuracy: NTP Pool servers are highly accurate, providing users with precise time information. This is crucial for various applications that rely on accurate timekeeping, such as financial transactions, logging, and data analysis.
- Enhanced Network Performance: Synchronized clocks across a network contribute to improved network performance by reducing latency and jitter. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time communication, such as video conferencing and online gaming.
- Increased Security: Accurate time synchronization plays a vital role in security by enabling secure authentication and encryption protocols. This is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring secure communication across networks.
- Simplified Configuration: Using NTP Pool simplifies time synchronization for users, as they do not need to manually configure their devices to connect to specific time servers. The NTP Pool provides a readily available and reliable source of time information, eliminating the need for complex setup.
How NTP Pool Works

The NTP Pool is a distributed network of time servers that offer time synchronization services to the internet. It’s a global collaboration that provides a robust and reliable time source for devices around the world. This pool is comprised of numerous servers managed by volunteers, each contributing to the overall accuracy and availability of the network.
Time Synchronization Process
The NTP Pool utilizes the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the time of devices on the internet. The process involves a client device requesting time information from an NTP server. The server then sends back its time, which is highly accurate and synchronized with other servers in the pool.
- Client Request: A device (client) needing time synchronization sends a request to an NTP server.
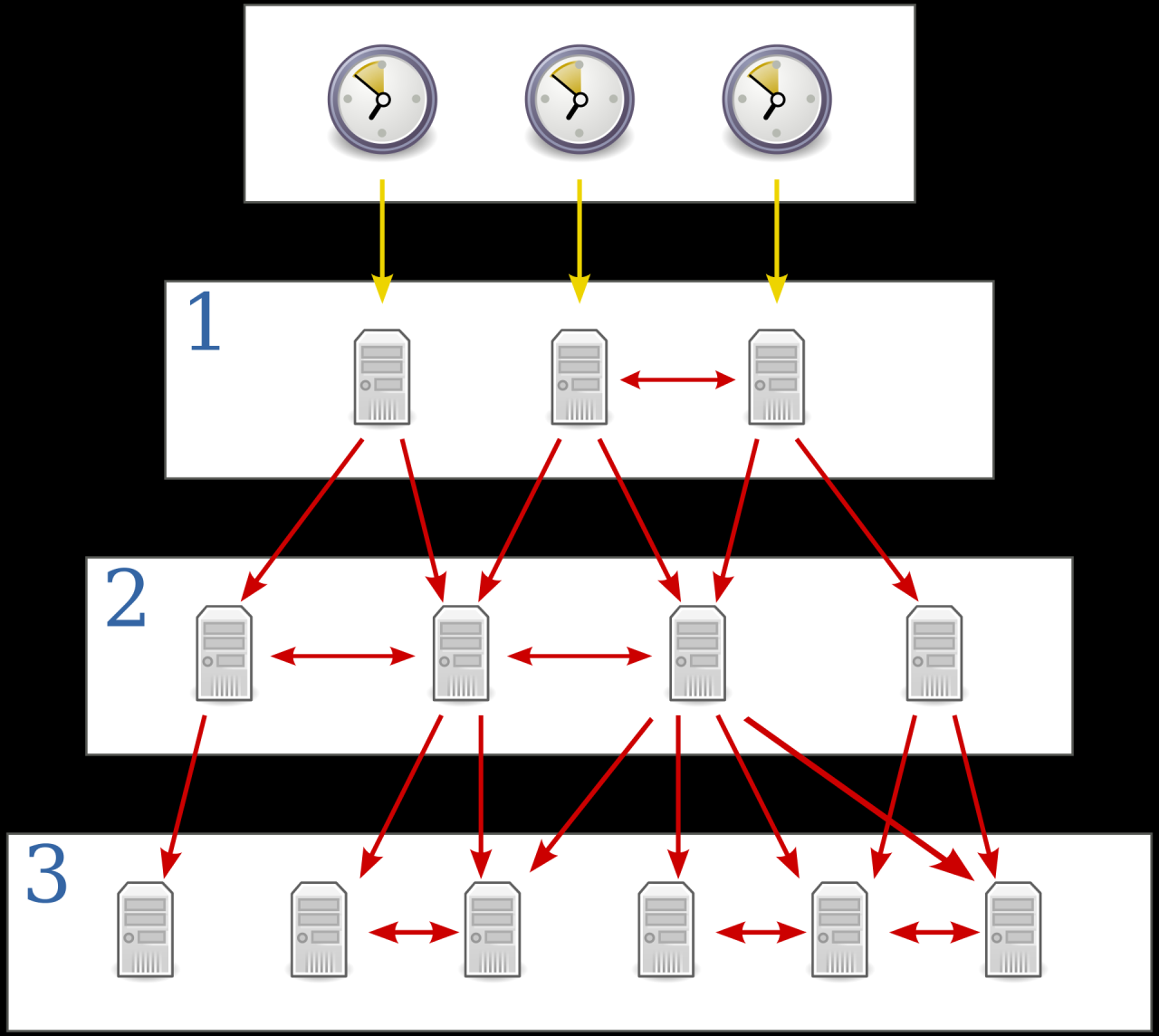
- Server Response: The NTP server responds with its current time, along with other information, such as the time offset and the server’s stratum level. Stratum level refers to the server’s position in the hierarchy of time sources. Servers directly connected to a reference clock have stratum 1, while those synchronized with stratum 1 servers have stratum 2, and so on.
- Time Adjustment: The client compares the received time with its own internal clock and adjusts its time accordingly. The adjustment process may involve adding or subtracting time to synchronize the client’s clock with the server’s time.
- Periodic Updates: The client periodically contacts the server to maintain synchronization. The frequency of updates depends on the client’s requirements for time accuracy and the network conditions.
Types of NTP Servers
There are different types of NTP servers within the NTP Pool, each playing a specific role in maintaining the pool’s accuracy and reliability:
- Reference Clocks: These servers are directly connected to high-precision time sources, such as atomic clocks. They are considered the most accurate time sources in the NTP Pool and have a stratum level of 1.
- Primary Servers: These servers are synchronized with reference clocks and have a stratum level of 2. They serve as primary time sources for other servers in the pool.
- Secondary Servers: These servers are synchronized with primary servers and have a stratum level greater than 2. They provide time synchronization services to clients on the internet.
Communication Protocols
The NTP Pool utilizes the Network Time Protocol (NTP) for communication between servers and clients. NTP is a UDP-based protocol that operates on port 123. The protocol uses a client-server architecture where clients request time information from servers.
NTP employs a sophisticated algorithm to determine the most accurate time source and minimize the impact of network delays and errors.
Setting Up NTP Pool
Using the NTP Pool is a simple process that involves configuring your device to connect to the NTP servers within the pool. This ensures that your device’s time is synchronized with accurate and reliable time sources, crucial for various operations, including network communication, data logging, and security.
An NTP pool is a collection of servers that help synchronize clocks across a network. It’s like a group of people all looking at the same clock, ensuring everyone is on the same page. This is especially important for applications that require precise timing, like financial transactions or even the delicate art of making bows , where a slight delay could ruin the perfect symmetry.
Just as a well-timed bow adds elegance to a gift, an NTP pool ensures accurate timekeeping across your network.
Configuring Devices to Use NTP Pool Servers
To use NTP Pool servers, you need to configure your device to communicate with them. This involves specifying the NTP server addresses in your system’s network settings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the NTP Server Address: The NTP Pool provides a simple way to find the appropriate server address for your location. You can use the website https://www.pool.ntp.org/ and enter your location to find the recommended server address. For example, for the United States, you can use “0.pool.ntp.org.”
- Access System Settings: The specific steps to access network settings vary depending on your operating system. For Windows, you can access the Network and Sharing Center, while for Linux systems, you can use the Network Manager or command-line tools. For macOS, you can access the Network preferences.
- Configure NTP Settings: Within the network settings, you’ll find options related to time synchronization. You can specify the NTP server address here. Typically, you’ll need to provide the server address and possibly the port number (usually 123).
- Save and Restart: After configuring the NTP server address, save the changes and restart your device to apply the settings. This ensures that the new configuration takes effect.
NTP Pool Configuration Examples
Here are examples of configuring NTP Pool servers for different operating systems:
- Windows: In the Network and Sharing Center, click on “Change adapter settings.” Right-click on your network connection and select “Properties.” Choose “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click on “Properties.” In the “General” tab, select “Obtain DNS server address automatically.” You can also manually specify the NTP server address in the “Preferred DNS server” field, such as “0.pool.ntp.org.”
- Linux (Ubuntu): Use the command
sudo timedatectl set-ntp 0.pool.ntp.orgto configure the NTP server address. You can also use the/etc/ntp.conffile to configure the NTP server. For example, you can add the lineserver 0.pool.ntp.orgto the file. - macOS: Open System Preferences and select “Network.” Choose your network connection and click on “Advanced.” Go to the “DNS” tab and add “0.pool.ntp.org” as a DNS server.
Choosing the Right NTP Server
When selecting an NTP server, it’s important to consider several factors:
- Location: Choosing an NTP server geographically closer to you minimizes latency and ensures faster time synchronization.
- Reliability: The NTP Pool offers reliable servers that are continuously monitored and maintained. However, it’s essential to ensure that the chosen server is up and running.
- Security: Ensure that the NTP server you select uses appropriate security measures to protect against attacks. The NTP Pool servers generally implement strong security practices.
NTP Pool Server Types
The NTP Pool relies on a diverse set of servers, each fulfilling a specific role in maintaining the network’s time accuracy. Understanding the server types helps in selecting the most suitable option for different use cases.
Server Types and Their Characteristics
The NTP Pool encompasses various server types, each with distinct capabilities and roles. The following table provides a comprehensive overview:
| Server Type | Description | Capabilities | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Server | These servers are typically located at high-quality time sources, such as atomic clocks or GPS receivers. | – High accuracy timekeeping – Synchronization with external time sources |
– Provide the most accurate time to the network |
| Secondary Server | These servers synchronize their time with primary servers and act as intermediaries for other servers within the pool. | – Receive time from primary servers – Distribute time to other servers |
– Facilitate time dissemination within the pool |
| Tertiary Server | These servers obtain their time from secondary servers and are typically located closer to end users. | – Receive time from secondary servers – Serve time to clients |
– Provide time to clients within the network |
| Relay Server | These servers act as intermediaries between clients and other servers within the pool, improving efficiency and reducing network traffic. | – Forward time requests to other servers – Cache time data for faster retrieval |
– Optimize time distribution and reduce network load |
Selecting a Suitable Server Type
The choice of server type depends on various factors, including:
– Accuracy requirements: For applications demanding high accuracy, primary servers are preferred.
– Location and network connectivity: Secondary and tertiary servers are often chosen based on their proximity to clients and network connectivity.
– Performance and load: Relay servers are ideal for handling high volumes of client requests and reducing network traffic.
For example, a financial institution with stringent time accuracy requirements would likely utilize primary servers for critical applications, while a small office network might rely on tertiary servers for general timekeeping.
NTP Pool Security
While the NTP Pool offers a convenient and reliable way to synchronize time across devices, it’s essential to understand the security implications and take appropriate measures to mitigate potential risks.
Secure NTP Protocols and Configurations
Using secure NTP protocols and configurations is crucial for protecting your network and devices from attacks.
- Use NTPv4: The latest version of the NTP protocol, NTPv4, offers enhanced security features like authentication and encryption. It is recommended to configure your devices to use NTPv4 whenever possible.
- Enable Authentication: Authentication helps verify the authenticity of NTP servers and prevents unauthorized access. You can enable authentication by configuring your devices to use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) authentication key.
- Restrict Access: Limit access to your NTP servers by configuring firewall rules to allow only authorized devices to connect. This can help prevent unauthorized access and potential attacks.
- Use Strong Passwords: If you’re managing your own NTP server, ensure you use strong passwords to protect it from unauthorized access.
NTP Pool Monitoring and Management
Keeping an NTP Pool running smoothly requires continuous monitoring and management. This ensures accurate time synchronization across the network and helps identify and address potential issues before they impact the pool’s performance.
Tools and Methods for Monitoring NTP Pool Servers
Monitoring tools provide insights into the health and performance of NTP Pool servers. This helps identify potential issues and take corrective measures promptly.
- NTP Monitoring Software: Tools like ntpstat, ntpq, and ntpdc provide detailed information about the NTP server’s configuration, status, and performance. They can be used to monitor:
- Server Load: Monitors the number of clients connected and the frequency of requests. High load can indicate potential performance issues.
- Time Accuracy: Tracks the server’s time offset and jitter, ensuring it’s within acceptable limits.
- Network Connectivity: Checks the server’s connection to other NTP servers and clients.
- Error Messages: Identifies and analyzes error messages to pinpoint potential problems.
- System Monitoring Tools: General system monitoring tools like Nagios, Zabbix, and Prometheus can be configured to monitor NTP server metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. This helps detect resource constraints that could impact performance.
- Log Analysis: Regularly reviewing server logs for error messages, warnings, and unusual activity helps identify and troubleshoot potential problems.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for ensuring reliable time synchronization across the network.
- Proactive Issue Detection: Early detection of performance issues allows for timely intervention, preventing major disruptions to time synchronization.
- Performance Optimization: Monitoring helps identify areas for improvement, such as optimizing server configuration or upgrading hardware.
- Security Enhancement: Regular security checks help identify and address vulnerabilities, protecting the pool from malicious attacks.
- Compliance with Standards: Monitoring ensures the pool adheres to industry standards and best practices for time synchronization.
Troubleshooting Common NTP Pool Issues
Troubleshooting NTP Pool issues involves analyzing error messages, checking server configuration, and verifying network connectivity.
- Time Offset and Jitter: If the server’s time offset or jitter is high, it could indicate problems with the server’s clock, network delays, or issues with the upstream NTP servers.
- Server Load: High server load can cause delays in responding to client requests, leading to inaccurate time synchronization.
- Network Connectivity: If the server is unable to connect to other NTP servers or clients, it will be unable to synchronize its time accurately.
- Configuration Errors: Incorrect server configuration, such as incorrect time zone settings or incorrect peer addresses, can lead to synchronization issues.
NTP Pool Alternatives
While NTP Pool is a popular and reliable time synchronization solution, it might not be the best fit for all scenarios. This section explores alternative time synchronization solutions and their advantages and disadvantages, providing insights into when these alternatives might be more suitable.
Time Synchronization Protocols
Time synchronization protocols are the backbone of any time synchronization solution. NTP is a widely used protocol, but other protocols exist with distinct characteristics and applications.
- Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP): A simplified version of NTP, designed for clients that require less precise time synchronization. SNTP offers lower overhead but sacrifices accuracy and reliability.
- Precision Time Protocol (PTP): A high-precision time synchronization protocol used in industrial automation, telecommunications, and other applications requiring sub-millisecond accuracy. PTP uses hardware timestamps and dedicated network infrastructure for high accuracy.
- Network Time Protocol over TLS (NTPS): A secure version of NTP that encrypts time synchronization traffic over TLS, enhancing security and privacy. NTPS is ideal for environments where data security is paramount.
Time Synchronization Services
Several time synchronization services offer alternative solutions to NTP Pool. These services provide centralized time sources and manage the complexities of time synchronization, allowing users to focus on their core applications.
- Google Time Service: Google provides a free and public time synchronization service, offering high accuracy and reliability. This service is suitable for general-purpose time synchronization, particularly for applications that require reliable timekeeping.
- Microsoft Time Service: Microsoft offers a time synchronization service for Windows operating systems. This service is integrated with Windows and provides reliable time synchronization for Windows-based systems.
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) Servers: Dedicated NTP servers are available from various providers, offering managed time synchronization services with customized features and support. These servers are suitable for organizations with specific requirements for accuracy, security, or support.
Time Synchronization Devices
Hardware-based time synchronization devices provide a physical solution for time synchronization. These devices are typically used in environments where accuracy and reliability are critical, such as financial institutions, telecommunications networks, and industrial control systems.
- GPS Time Receivers: These devices receive time signals from GPS satellites, providing highly accurate and reliable time synchronization. GPS receivers are suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and redundancy.
- Radio Clocks: Radio clocks receive time signals from atomic clocks broadcasted over radio frequencies, providing highly accurate and reliable time synchronization. Radio clocks are suitable for environments where GPS reception is unreliable.
Time Synchronization Software
Time synchronization software offers a flexible and customizable approach to time synchronization. These software solutions provide tools for managing time synchronization, configuring servers, and monitoring performance.
- NTP Software Packages: Several NTP software packages are available for various operating systems, providing open-source and commercial options. These packages offer customizable features and support for specific environments.
- Time Synchronization Management Software: Specialized software solutions focus on managing time synchronization across large networks, providing centralized control, monitoring, and reporting capabilities. These solutions are suitable for organizations with complex time synchronization requirements.
Real-World Applications of NTP Pool
The NTP Pool, a global network of time servers, plays a vital role in synchronizing clocks across various devices and systems. Its widespread adoption stems from its ability to provide accurate and reliable timekeeping for a multitude of applications in different industries. This section explores the diverse use cases of NTP Pool, highlighting its importance in critical time-sensitive operations and the impact of precise time synchronization in various environments.
Financial Transactions
Accurate time synchronization is paramount in the financial industry, where transactions occur at lightning speed. NTP Pool ensures that financial systems across different locations are synchronized, preventing discrepancies in timestamps that could lead to fraud or disputes. For instance, in stock trading, timestamps are used to determine the order of trades, and any discrepancies could result in significant financial losses.
Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry heavily relies on NTP Pool for accurate time synchronization. Network devices like routers, switches, and base stations require precise timekeeping for tasks such as call routing, network management, and billing. NTP Pool ensures that these devices operate in sync, preventing delays, call drops, and other network issues.
Scientific Research
Scientific research often involves experiments and observations that require precise time measurements. NTP Pool plays a crucial role in synchronizing instruments, data acquisition systems, and other equipment used in scientific research. This ensures that data collected from different locations is time-stamped accurately, enabling scientists to analyze and interpret results with confidence.
Power Grid Management
Time synchronization is essential for the reliable operation of power grids. NTP Pool ensures that power generation and distribution systems are synchronized, preventing cascading failures and ensuring a stable supply of electricity. Accurate timekeeping is critical for tasks such as load balancing, frequency control, and protection relays.
Air Traffic Control
Air traffic control systems rely on precise time synchronization for aircraft tracking, communication, and collision avoidance. NTP Pool ensures that air traffic control towers, radar systems, and aircraft navigation equipment are synchronized, preventing delays, accidents, and airspace conflicts.
Cybersecurity
NTP Pool plays a vital role in cybersecurity by providing accurate timestamps for logging and auditing events. This helps security professionals to track and analyze security incidents, identify potential threats, and respond effectively to cyberattacks. Accurate timestamps are also essential for forensic investigations, allowing investigators to determine the sequence of events and identify perpetrators.
The Future of NTP Pool
The NTP Pool, a vital resource for accurate time synchronization, is constantly evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing technological landscape. As we move forward, we can expect to see advancements that enhance its capabilities, address emerging challenges, and integrate seamlessly with new technologies.
Advancements in NTP Pool Technology
The future of the NTP Pool holds exciting advancements in technology. These developments aim to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and security while addressing emerging challenges in time synchronization.
- Improved Time Accuracy: Ongoing research focuses on refining the NTP protocol to achieve even greater time accuracy. This includes exploring techniques like using multiple reference clocks and advanced filtering algorithms to minimize errors and improve precision.
- Enhanced Network Efficiency: Future efforts will focus on optimizing the network infrastructure used by the NTP Pool to reduce latency and improve efficiency. This may involve exploring new routing protocols, load balancing techniques, and distributed systems architectures.
- Increased Security Measures: As cyber threats evolve, the NTP Pool will continue to enhance its security measures. This includes implementing stronger authentication protocols, advanced intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits to protect against attacks and data breaches.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: The NTP Pool is expected to seamlessly integrate with emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and 5G networks. This will enable time synchronization for a wider range of devices and applications, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of time-critical operations.
Emerging Trends in Time Synchronization
The landscape of time synchronization is constantly evolving, driven by the increasing reliance on time-critical applications and the rise of new technologies.
- The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of interconnected devices in the IoT presents a significant challenge for time synchronization. The vast number of devices, their diverse nature, and the need for real-time communication necessitate robust and scalable time synchronization solutions. The NTP Pool is well-positioned to address this challenge, providing a reliable and accessible time source for IoT devices.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology: Blockchain technology relies heavily on accurate timestamps to ensure the integrity and immutability of transactions. The NTP Pool can play a critical role in providing accurate time for blockchain networks, contributing to their security and reliability.
- 5G Networks and Edge Computing: The advent of 5G networks and edge computing introduces new demands for time synchronization. The high-speed data transfer and low latency requirements of 5G networks require precise time synchronization for efficient operation. The NTP Pool can provide the necessary time accuracy for these applications, ensuring smooth data flow and reliable communication.
Impact of New Technologies on NTP Pool
New technologies have the potential to significantly impact the NTP Pool, creating both opportunities and challenges.
- Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud computing has increased the demand for time synchronization services. The NTP Pool can leverage cloud platforms to provide scalable and readily accessible time synchronization services for cloud-based applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms often require precise time synchronization for tasks like data analysis and machine learning. The NTP Pool can provide the necessary time accuracy for AI applications, enabling more efficient and reliable AI systems.
Best Practices for Using NTP Pool
Ensuring accurate time synchronization is crucial for network operations, and the NTP Pool provides a reliable and accessible solution. This section Artikels best practices for configuring and using NTP Pool servers to maximize performance and security.
Configuring NTP Pool Servers
Proper configuration of NTP Pool servers is essential for optimal performance and security. Here are some key considerations:
- Choose the Right Server Type: NTP Pool offers different server types, each with its own capabilities. Select the type that best suits your needs, considering factors like available resources, security requirements, and the number of clients to be served.
- Set Up a Secure Network: Ensure your NTP Pool server is located on a secure network, protected from unauthorized access. Implement strong firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control measures to safeguard the server from malicious activities.
- Use Strong Authentication: Employ strong authentication mechanisms, such as password-based authentication or digital certificates, to restrict access to the NTP Pool server. This helps prevent unauthorized users from manipulating time settings.
- Configure Time Zones: Carefully configure the time zone for your NTP Pool server to ensure accurate time synchronization for all clients. Consider using the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) as the default time zone.
- Set Appropriate Timeouts: Configure appropriate timeouts for communication between clients and the NTP Pool server. This prevents clients from waiting indefinitely for a response, ensuring timely synchronization.
Optimizing Performance
Optimizing NTP Pool performance is critical for maintaining accurate time synchronization across your network. Consider these strategies:
- Minimize Network Latency: Reduce network latency between clients and the NTP Pool server by choosing a geographically close server or optimizing network performance. Lower latency improves the accuracy of time synchronization.
- Use a Redundant Server Configuration: Implement a redundant server configuration, with multiple NTP Pool servers, to ensure continuous time synchronization even if one server fails. This provides high availability and minimizes disruptions.
- Limit the Number of Clients: While NTP Pool servers are designed to handle multiple clients, limiting the number of clients per server can improve performance. Distribute clients across multiple servers to ensure optimal response times.
- Monitor Server Load: Regularly monitor the load on your NTP Pool servers to identify potential bottlenecks and adjust server configuration accordingly. This helps ensure efficient operation and prevent performance degradation.
Security Best Practices, Ntp pool
Maintaining the security of your NTP Pool servers is paramount to protect against unauthorized access and malicious activities. Follow these security best practices:
- Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update your NTP Pool server software to patch vulnerabilities and improve security. This includes installing the latest security updates and patches.
- Implement Access Control: Restrict access to the NTP Pool server to authorized users and devices. Implement strong password policies and access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitor for Security Threats: Regularly monitor your NTP Pool server for security threats, such as intrusion attempts or malware infections. Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to detect and mitigate threats.
- Use Secure Communication Protocols: Utilize secure communication protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Shell (SSH), to protect data transmission between clients and the NTP Pool server. This prevents eavesdropping and data manipulation.
Industry Standards and Guidelines
Adhering to industry standards and guidelines ensures interoperability, reliability, and security for your NTP Pool deployment. Follow these recommendations:
- Network Time Protocol (NTP): Follow the specifications Artikeld in the Network Time Protocol (NTP) standard. This ensures compatibility and interoperability with other NTP-compliant devices.
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF): Refer to the guidelines and best practices published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) for NTP deployment. These guidelines provide valuable insights into secure and efficient configuration.
- Security Best Practices: Implement security best practices recommended by security organizations, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). These practices help mitigate security risks and protect your NTP Pool servers.
Case Studies of NTP Pool Implementation
The effectiveness of NTP Pool can be best understood by examining real-world implementations and their impact. This section explores various case studies, highlighting the challenges encountered, solutions adopted, and benefits achieved through NTP Pool deployment.
Successful Implementations of NTP Pool
Several organizations have successfully leveraged NTP Pool to improve time synchronization across their networks. These implementations demonstrate the diverse applications and benefits of using NTP Pool.
- Large-Scale Enterprise Networks: Major corporations like Google, Amazon, and Facebook rely on NTP Pool to synchronize time across their vast infrastructure. This ensures accurate timestamping of data, improves application performance, and enhances security by preventing replay attacks.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial institutions rely on precise time synchronization for regulatory compliance and fraud prevention. NTP Pool provides a robust and reliable time source for critical applications like trading systems and transaction processing.
- Scientific Research: Research institutions involved in experiments requiring high-precision time synchronization often utilize NTP Pool. This ensures accurate measurements and analysis of data, leading to more reliable scientific findings.
Challenges Faced and Solutions Adopted
Implementing NTP Pool can present unique challenges depending on the specific environment and requirements.
- Network Latency: High network latency can affect time synchronization accuracy. To mitigate this, organizations can strategically place NTP servers closer to their clients or use dedicated high-bandwidth connections.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring the security of NTP servers is crucial. Organizations can implement access control lists, firewalls, and encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential attacks.
- Scalability: As the network grows, the number of clients requiring time synchronization increases. NTP Pool offers a scalable solution, with multiple servers and redundancy mechanisms to handle high client loads.
Benefits Achieved through NTP Pool Deployment
Deploying NTP Pool offers significant benefits for organizations of all sizes.
- Improved Time Synchronization Accuracy: NTP Pool provides a highly accurate and reliable time source, ensuring precise time synchronization across the network.
- Enhanced Application Performance: Accurate time synchronization improves the performance of various applications, including databases, web servers, and network monitoring tools.
- Increased Security: NTP Pool helps prevent replay attacks and other security threats by ensuring accurate timestamping of data.
- Reduced Costs: NTP Pool is a cost-effective solution compared to maintaining a dedicated internal NTP server infrastructure.
Case Study: NTP Pool Implementation at a University
A large university deployed NTP Pool to synchronize time across its campus network, encompassing thousands of computers and devices. The university faced challenges with inconsistent time synchronization, leading to issues with application performance and security. By implementing NTP Pool, the university achieved the following:
- Improved Time Synchronization Accuracy: NTP Pool ensured consistent time synchronization across the campus network, eliminating time discrepancies and improving application performance.
- Enhanced Security: The university’s security posture was strengthened by preventing replay attacks and other security threats that exploit time synchronization vulnerabilities.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: By leveraging NTP Pool, the university eliminated the need to maintain a dedicated internal NTP server infrastructure, reducing operational costs.
Final Review: Ntp Pool
NTP Pool is a testament to the collaborative spirit of the internet community, providing a vital service for time synchronization. Its impact extends far beyond individual computers, ensuring the smooth operation of countless applications and services that rely on accurate timekeeping. From financial transactions to scientific research, NTP Pool plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of our digital world.