Esx server – ESXi server is a powerful virtualization platform that enables organizations to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical server. This technology allows for efficient resource utilization, improved performance, and enhanced flexibility, making it a cornerstone of modern data centers and cloud environments.
ESXi, the core component of VMware’s vSphere suite, offers a streamlined approach to virtualization. It operates as a bare-metal hypervisor, directly managing hardware resources without the need for an underlying operating system. This lean architecture provides a secure and efficient foundation for running virtual machines.
ESXi Server Overview
ESXi, short for VMware ESXi, is a type of hypervisor software that allows you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. This virtualization technology enables efficient resource utilization, reduces hardware costs, and simplifies server management.
ESXi vs. ESX
ESXi and ESX are both virtualization platforms developed by VMware. The key difference lies in their architecture:
- ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor, meaning it runs directly on the server’s hardware without an underlying operating system. This makes it more lightweight and efficient than ESX.
- ESX, on the other hand, is a hosted hypervisor, which requires a separate operating system (such as Linux) to run. This architecture adds an extra layer of complexity and resource consumption.
ESXi emerged as the successor to ESX, offering enhanced performance, security, and ease of management. Today, ESXi is the dominant virtualization platform used by VMware.
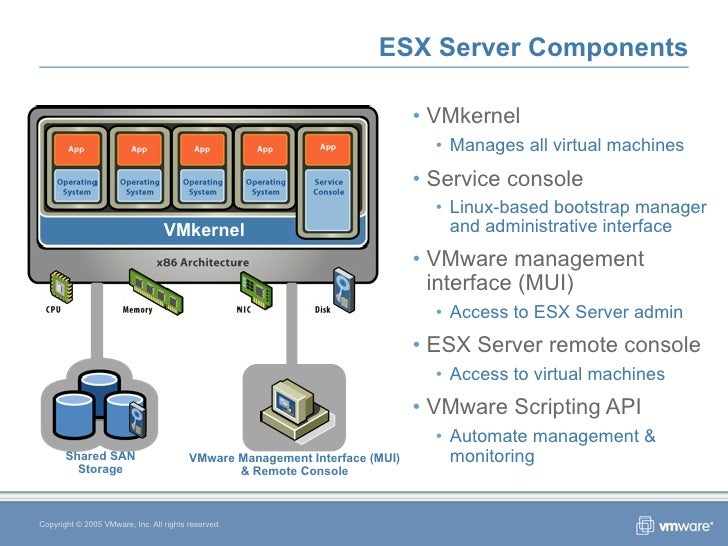
Core Components of ESXi Server Architecture
ESXi server architecture consists of several key components:
- VMkernel: This is the core of the ESXi operating system. It manages the hardware resources, network communication, and virtualization functions.
- Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM): The VMM is responsible for isolating and managing virtual machines, providing a secure and independent environment for each VM.
- Storage Management: ESXi supports various storage technologies, including local disks, SANs, and NAS. It provides mechanisms for managing storage space, creating virtual disks, and ensuring data integrity.
- Networking: ESXi offers robust networking capabilities, including support for various network protocols, virtual networking, and network security features.
- Management Interface: ESXi provides a web-based interface (vSphere Client) and a command-line interface (ESXi Shell) for managing the server and its virtual machines.
ESXi Server Installation and Configuration
Installing and configuring ESXi server on a physical host involves several steps, ensuring proper setup for virtualized environments. This section will cover the essential steps for ESXi installation and basic configuration, including networking, storage, and security.
ESXi Server Installation
ESXi server installation requires a bootable USB drive or ISO image containing the ESXi installer. The installation process involves booting from the installation media and following the on-screen instructions. Here’s a breakdown of the steps:
- Download ESXi Installer: Obtain the ESXi installer from the VMware website, selecting the appropriate version for your hardware.
- Create Bootable Media: Create a bootable USB drive or burn an ISO image to a CD/DVD. Refer to VMware documentation for detailed instructions on creating bootable media.
- Boot from Installation Media: Configure the BIOS of the physical host to boot from the USB drive or CD/DVD.
- Select Installation Options: Choose the appropriate installation options, such as language, keyboard layout, and network settings.
- Accept License Agreement: Review and accept the ESXi license agreement.
- Configure Storage: Select the storage device where ESXi will be installed.
- Set Root Password: Choose a strong password for the ESXi root account.
- Complete Installation: The installation process will take some time to complete. Once finished, the ESXi server will reboot.
ESXi Server Basic Configuration
Once the ESXi server is installed, it’s crucial to configure basic settings for networking, storage, and security. These configurations ensure proper connectivity, data management, and system protection.
Networking Configuration
- Network Interface Configuration: Configure the network interfaces on the ESXi server, assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways. This step is crucial for accessing the ESXi server remotely and connecting virtual machines to the network.
- VLAN Configuration (Optional): If using VLANs, configure the ESXi server to support the required VLANs and assign virtual machines to specific VLANs.
- Network Security: Configure firewall rules and network access control lists (ACLs) to restrict unauthorized access to the ESXi server.
Storage Configuration
- Storage Device Management: Manage storage devices attached to the ESXi server, creating datastores for storing virtual machine files and other data.
- Storage Access Control: Configure storage access permissions to control which virtual machines can access specific datastores.
- Storage Performance Optimization: Optimize storage performance by configuring RAID levels, using appropriate disk types, and implementing caching mechanisms.
Security Configuration
- Password Policies: Set strong password policies for the ESXi root account and other administrative accounts.
- SSH Access Control: Configure SSH access to the ESXi server, limiting access to authorized users and using SSH keys for secure authentication.
- Security Updates: Regularly apply security updates and patches to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure the ESXi server’s security.
ESXi Server Hardening and Security Measures
Hardening an ESXi server involves implementing security measures to minimize vulnerabilities and protect against unauthorized access.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable services that are not required for the ESXi server’s operation to reduce potential attack vectors.
- Lock Down Ports: Configure firewall rules to block access to unnecessary ports and services.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong passwords for all accounts, including the ESXi root account and any administrative accounts.
- Enable Security Features: Enable security features like Secure Boot, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), and Virtual Machine Integrity (VMI) to enhance system security.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate the ESXi server from other networks and systems to minimize the impact of potential attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Virtual Machine Management
Virtual machines (VMs) are the core of virtualization, and managing them effectively is crucial for optimal performance and resource utilization. ESXi provides a comprehensive set of tools and features for creating, deploying, and managing VMs.
Creating and Deploying Virtual Machines
Creating a VM in ESXi involves defining its hardware configuration, specifying the operating system, and choosing the storage location. The process can be initiated through the ESXi host’s web interface or using the vSphere Client.
- Define Hardware Configuration: This step involves specifying the VM’s resources, including CPU cores, RAM, and storage space. These settings determine the VM’s performance and capabilities.
- Select Operating System: Choose the operating system that will run on the VM. ESXi supports various operating systems, from popular Linux distributions to Windows server editions.
- Storage Location: Specify the storage location for the VM’s virtual disk files. This can be a local datastore on the ESXi host or a shared storage solution like NFS or iSCSI.
- Network Configuration: Configure the VM’s network settings, including its IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. This enables the VM to communicate with other devices on the network.
Virtual Machine Configurations
VM configurations encompass the various hardware resources allocated to each VM, including memory, CPU, and storage. These settings directly impact the VM’s performance and capabilities.
Memory Configuration
The amount of RAM allocated to a VM is a critical factor in its performance. Adequate memory ensures smooth operation and prevents performance bottlenecks. ESXi offers various memory allocation options:
- Static RAM: This option reserves a fixed amount of RAM for the VM, ensuring consistent performance. However, it can lead to wasted resources if the VM doesn’t utilize all the allocated memory.
- Dynamic RAM: This option allows the VM to dynamically adjust its RAM usage based on demand. This can optimize resource utilization but might result in performance fluctuations if the VM experiences memory pressure.
- Memory Ballooning: This feature allows ESXi to reclaim unused RAM from VMs, making it available for other VMs. This can improve overall resource utilization, but it might impact the performance of the ballooned VM if it experiences memory pressure.
CPU Configuration
The number of CPU cores allocated to a VM determines its processing power. ESXi provides options for configuring the VM’s CPU resources:
- CPU Cores: Specify the number of CPU cores to be allocated to the VM. This directly impacts the VM’s processing capabilities.
- CPU Shares: This option allows you to control the relative CPU resources allocated to different VMs. This is particularly useful for managing workloads with varying resource requirements.
- CPU Reservations: This option guarantees a minimum amount of CPU resources for the VM, ensuring consistent performance even under high load.
Storage Configuration
Storage configuration involves choosing the appropriate storage solution and defining the virtual disk settings for the VM. ESXi offers various storage options:
- Local Datastore: This option stores the VM’s virtual disk files on the ESXi host’s local storage. It is suitable for small deployments or VMs with minimal storage requirements.
- Shared Storage: This option uses a shared storage solution, such as NFS or iSCSI, to store the VM’s virtual disk files. This enables centralized storage management and provides high availability.
- Virtual Disk Types: ESXi supports various virtual disk types, including thick provisioned, thin provisioned, and eager zeroed thick provisioned. Each type has its own performance and storage efficiency characteristics.
Managing VM Resources and Performance Optimization
Effective VM resource management and performance optimization are essential for ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization within the virtualized environment.
Resource Monitoring and Analysis
Regular monitoring of VM resources is crucial for identifying potential performance bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation. ESXi provides tools for monitoring VM metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and storage I/O. This data can be analyzed to identify resource-intensive VMs and adjust their configurations accordingly.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Various techniques can be employed to optimize VM performance:
- Resource Allocation: Ensure adequate resources are allocated to VMs based on their workloads and performance requirements.
- VM Consolidation: Combine multiple VMs onto a single host to improve resource utilization and reduce hardware costs.
- Storage Optimization: Optimize storage performance by using appropriate storage solutions, configuring virtual disks efficiently, and implementing storage caching mechanisms.
- Network Optimization: Optimize network performance by using appropriate network configurations, implementing network bonding, and reducing network traffic.
ESXi Server Storage Management: Esx Server
ESXi Server storage management is crucial for ensuring the performance and reliability of your virtualized environment. Choosing the right storage solution and effectively managing storage capacity and performance are essential for optimal results.
Storage Options
ESXi servers offer various storage options to meet diverse needs. These options can be categorized into local storage, SAN, and NAS.
- Local Storage: This option uses the physical storage devices directly attached to the ESXi host. Local storage is simple to configure and can be cost-effective, but it can be limiting in terms of scalability and redundancy. It is often suitable for small deployments or testing environments.
- SAN (Storage Area Network): A SAN provides high-speed, block-level access to shared storage resources. It allows multiple servers to access the same storage pool, enabling centralized management and high availability. SANs are typically used in large enterprise environments where high performance and scalability are essential.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage): A NAS offers file-level access to shared storage resources over a network. It is a more cost-effective option compared to SANs, but it provides lower performance. NAS is suitable for applications that require file-level access, such as backups and data sharing.
Storage vMotion
Storage vMotion is a powerful feature that allows you to migrate running virtual machines from one storage location to another without downtime. This feature is particularly useful for:
- Storage upgrades: Migrating VMs to a new storage array or to a different type of storage.
- Storage maintenance: Performing maintenance tasks on the storage infrastructure without impacting running VMs.
- Disaster recovery: Moving VMs to a different location for redundancy and disaster recovery purposes.
Storage Capacity and Performance Management
Managing storage capacity and performance effectively is crucial for maintaining a healthy virtualized environment. Here are some best practices:
- Monitor storage usage: Regularly monitor storage capacity and utilization to identify potential bottlenecks and plan for future growth.
- Optimize storage performance: Use tools and techniques to optimize storage performance, such as RAID configurations, caching, and storage tiering.
- Implement storage policies: Define storage policies to ensure that VMs are provisioned with appropriate storage resources based on their requirements.
- Use storage snapshots: Create regular storage snapshots to provide backups and restore points in case of data loss or corruption.
ESXi Server Networking
ESXi Server networking plays a crucial role in connecting virtual machines to the physical network and ensuring efficient data flow. It offers various configurations to meet different requirements, including VLANs, port groups, and distributed switches.
VLANs
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) are a key component of ESXi server networking, enabling the logical segmentation of a physical network into multiple broadcast domains. VLANs are used to isolate traffic between different groups of users or applications, enhancing security and network performance.
- VLAN Tagging: VLANs use tags to identify traffic belonging to a specific VLAN. These tags are added to Ethernet frames during transmission, allowing network devices to filter and forward traffic based on VLAN membership.
- VLAN Trunking: VLAN trunking allows multiple VLANs to share a single physical link. This is achieved using protocols like 802.1q, which encapsulate VLAN tags within Ethernet frames.
- VLAN Benefits:
- Improved Security: VLANs isolate traffic between different groups, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Enhanced Network Performance: VLANs reduce network congestion by segmenting traffic and limiting broadcasts.
- Flexible Network Management: VLANs allow administrators to easily configure and manage network access for different users and applications.
Port Groups
Port groups are logical entities within ESXi servers that group physical network interfaces (NICs) and define network settings for virtual machines.
- Port Group Configuration: When creating a port group, administrators specify settings such as VLAN ID, network address, and security policies.
- Virtual Machine Network Connectivity: Virtual machines connect to the physical network through port groups. Each virtual machine can be assigned to a specific port group, ensuring that it has access to the appropriate network resources.
- Port Group Types: ESXi servers support various port group types, including:
- Standard Port Groups: These are basic port groups that provide connectivity to virtual machines.
- Distributed Port Groups: These are managed by vSphere Distributed Switches and offer advanced features like load balancing and security.
vSphere Distributed Switch
vSphere Distributed Switch is a virtual networking platform that simplifies and centralizes network management for multiple ESXi hosts. It provides advanced features and capabilities, including:
- Centralized Management: vSphere Distributed Switch allows administrators to manage network settings from a single point, eliminating the need to configure each ESXi host individually.
- Load Balancing: Distributed switches can distribute network traffic across multiple uplinks, improving network performance and redundancy.
- Security: Distributed switches offer advanced security features, such as port security, MAC address filtering, and network access control (NAC).
- High Availability: Distributed switches provide high availability through features like link aggregation and failover, ensuring continuous network connectivity.
ESXi Server Networking Best Practices
- Plan Your Network: Carefully plan your network topology and design before implementing any changes. This includes defining VLANs, port groups, and distributed switch configurations.
- Use VLANs: Utilize VLANs to segment traffic and enhance security. This helps isolate critical applications and sensitive data.
- Implement Distributed Switches: Leverage vSphere Distributed Switches for centralized management, load balancing, and advanced security features.
- Monitor Network Performance: Regularly monitor network performance metrics, such as latency, throughput, and error rates. This helps identify and resolve network bottlenecks.
- Implement Network Security: Implement appropriate security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and antivirus software.
ESXi Server Security
ESXi servers, being the foundation of virtualized environments, are critical targets for malicious actors. Understanding and mitigating security vulnerabilities is paramount to ensure the integrity and availability of your virtualized infrastructure.
Security Vulnerabilities and Threats
ESXi servers, like any software, are susceptible to security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive data. Common threats include:
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, can infect ESXi servers and compromise their functionality.
- Exploitation of Vulnerabilities: Attackers can exploit known vulnerabilities in ESXi software to gain unauthorized access or execute malicious code.
- Denial of Service Attacks: These attacks aim to overload ESXi servers with traffic, rendering them unavailable to legitimate users.
- Credential Theft: Attackers may attempt to steal administrator credentials, allowing them to gain full control over the ESXi server.
Built-in Security Features, Esx server
ESXi includes several built-in security features to protect against these threats:
- Firewall: The ESXi firewall acts as a barrier between the ESXi server and the outside world, blocking unauthorized network traffic.
- Lockdown Mode: Lockdown mode restricts access to the ESXi server, limiting the potential attack surface and enhancing security.
- Security Updates: VMware regularly releases security updates to address vulnerabilities and improve the security posture of ESXi servers. Applying these updates promptly is crucial.
Implementing Additional Security Measures
Beyond the built-in features, you can implement additional security measures to further enhance the protection of your ESXi servers:
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert you to potential attacks.
- Security Auditing: Regularly audit security logs to identify potential security breaches or suspicious activity.
- Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Use strong passwords and enable 2FA for administrator accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct periodic security assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate ESXi servers from other network segments to limit the impact of a successful attack.
- Secure Boot: Enable secure boot to ensure that only trusted software is loaded during the boot process.
- VMware vCenter Server Security: Secure vCenter Server, the central management platform for ESXi servers, as it is a critical target for attackers.
ESXi Server Monitoring and Management
Effective monitoring and management are crucial for ensuring the stability, performance, and security of your ESXi servers. By implementing appropriate tools and strategies, you can proactively identify and address potential issues, optimize resource utilization, and maintain a reliable virtualized environment.
ESXi Server Monitoring Tools and Methods
ESXi Server provides a variety of built-in tools and methods for monitoring server health and performance. These tools offer real-time insights into various aspects of the server’s operation, enabling you to quickly identify and address any anomalies or potential issues.
- vSphere Web Client: This web-based interface provides a comprehensive view of the ESXi server’s status, performance metrics, and configuration settings. It offers a user-friendly dashboard with customizable views, allowing you to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, and network traffic.
- ESXi Shell: The ESXi shell provides a command-line interface for interacting with the server and accessing its logs. It allows you to execute commands, retrieve system information, and troubleshoot issues. You can use the `esxtop` command to monitor real-time performance data, including CPU, memory, and network statistics.
- Performance Counters: ESXi Server exposes a range of performance counters that provide detailed information about various aspects of the server’s operation. These counters can be accessed through the vSphere Web Client or using tools like `esxtop`. By monitoring these counters, you can gain insights into CPU usage, memory allocation, disk I/O activity, and network traffic patterns.
- System Logs: ESXi Server maintains system logs that record events, errors, and warnings related to the server’s operation. These logs provide valuable information for troubleshooting issues and understanding the server’s behavior. You can access the system logs through the vSphere Web Client or using the ESXi shell.
vCenter Server for Centralized Management
vCenter Server acts as a central management platform for multiple ESXi servers, providing a unified view and control over the entire virtualized environment. It offers a comprehensive set of features for managing, monitoring, and automating tasks across your ESXi servers, simplifying administration and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Centralized Monitoring: vCenter Server consolidates monitoring data from all managed ESXi servers, providing a centralized dashboard for viewing performance metrics, system health, and resource utilization. This centralized view allows you to quickly identify and address potential issues across your entire virtualized environment.
- Automated Tasks: vCenter Server enables the automation of various tasks, such as provisioning virtual machines, managing storage, and applying security updates. This automation streamlines administrative processes, reduces manual intervention, and improves efficiency.
- Resource Management: vCenter Server provides tools for managing and optimizing resource allocation across your ESXi servers. It allows you to balance workloads, allocate resources effectively, and ensure optimal performance for your virtual machines.
- Security Management: vCenter Server offers comprehensive security features, including role-based access control, security policies, and vulnerability scanning. This helps to secure your virtualized environment and protect your data from unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Proactive Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Proactive monitoring and troubleshooting are essential for maintaining a stable and reliable virtualized environment. By implementing best practices, you can identify and address potential issues before they impact your critical applications and services.
- Establish Baselines: Establish baseline performance metrics for your ESXi servers based on historical data. This baseline provides a reference point for comparing current performance to identify any deviations or anomalies that may indicate potential issues.
- Set Alerts: Configure alerts for critical performance thresholds or system events. This ensures you are notified promptly of any potential issues, allowing you to take corrective action before they escalate.
- Regularly Review Logs: Regularly review system logs to identify any patterns or trends that may indicate potential issues. This proactive approach can help you address problems before they become major incidents.
- Conduct Regular Health Checks: Perform regular health checks on your ESXi servers to ensure they are operating within acceptable parameters. This includes checking CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network connectivity.
- Maintain Up-to-Date Software: Ensure that your ESXi servers are running the latest software versions, including patches and updates. This helps to mitigate security vulnerabilities and improve system stability.
- Document Procedures: Document your monitoring and troubleshooting procedures to ensure consistency and provide guidance for other administrators. This documentation can be helpful for onboarding new team members and maintaining a standardized approach to server management.
ESXi Server High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Ensuring continuous operation and data protection is paramount for any critical system, and ESXi servers are no exception. High availability (HA) and disaster recovery (DR) strategies are essential for mitigating downtime and data loss in the event of hardware failures, network outages, or other unforeseen events.
High Availability Techniques
High availability aims to minimize downtime by ensuring that critical services remain accessible even if a server component fails. ESXi servers offer several techniques to achieve high availability:
- vSphere HA: This feature automatically restarts virtual machines (VMs) on a different ESXi host in the cluster if the original host fails. vSphere HA monitors the health of ESXi hosts and VMs, detecting failures and triggering failover actions. It utilizes heartbeat signals to ensure that hosts are operational and communicating with each other.
- VMware Fault Tolerance (FT): FT provides a higher level of availability by creating a secondary, real-time replica of a VM on a different ESXi host. This replica runs in a locked-step synchronization with the primary VM, ensuring that if the primary host fails, the secondary VM instantly takes over. This eliminates the need for a restart and ensures zero downtime for the VM. FT is typically used for mission-critical applications requiring the highest levels of availability.
Disaster Recovery Solutions
Disaster recovery goes beyond minimizing downtime; it focuses on restoring the entire IT infrastructure in case of a catastrophic event that affects multiple systems. This includes restoring data, applications, and the operating environment.
- Replication Technologies: Solutions like VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) enable the replication of VMs to a remote site. In case of a disaster, these replicated VMs can be quickly powered on at the secondary site, minimizing downtime. SRM also automates the failover process, simplifying the recovery effort.
- Backup and Restore: Regular backups of data and configurations are essential for any DR strategy. Backups should be stored offsite to ensure they are protected from the same disaster that affects the primary site.
Best Practices for Designing and Implementing Disaster Recovery Solutions
Designing a robust disaster recovery solution involves considering several factors:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This defines the maximum allowable downtime before critical services must be restored.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This defines the maximum acceptable data loss in case of a disaster.
- Replication Strategy: Choose a replication solution that meets the RTO and RPO requirements.
- Testing and Validation: Regular testing of the DR plan is crucial to ensure it is effective and to identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
ESXi Server Virtualization Technologies
ESXi Server offers various virtualization technologies that enhance flexibility, efficiency, and resource utilization in virtualized environments. These technologies enable seamless migration, replication, and high availability, allowing administrators to manage virtual machines with ease.
vSphere vMotion
vSphere vMotion facilitates the live migration of running virtual machines from one physical host to another without any downtime or interruption to users. This technology enables administrators to perform maintenance tasks on ESXi hosts, upgrade hardware, or relocate virtual machines to different locations without affecting user productivity.
- Benefits: vMotion minimizes downtime, improves server utilization, and facilitates planned maintenance activities. It allows for flexible resource allocation and can be used to balance workloads across multiple ESXi hosts.
- Limitations: vMotion requires compatible hardware on both source and destination hosts. It also requires sufficient network bandwidth to handle the data transfer during migration. The virtual machine’s storage must be shared between the source and destination hosts.
- Example: An organization needs to perform maintenance on a physical server hosting a critical application. Using vMotion, they can seamlessly migrate the virtual machine running the application to another ESXi host, allowing maintenance to proceed without interrupting user access.
Storage vMotion
Storage vMotion enables the live migration of virtual machine disks from one storage location to another without downtime or service interruption. This technology facilitates storage upgrades, consolidation, or relocation of virtual machine disks to different storage devices.
- Benefits: Storage vMotion allows for flexible storage management, enables storage upgrades without downtime, and optimizes storage utilization by consolidating data to specific storage locations.
- Limitations: Storage vMotion requires compatible storage systems and network connectivity between the source and destination storage locations. It also requires sufficient bandwidth to handle the data transfer during migration.
- Example: An organization needs to upgrade the storage system for their virtual machines. Using Storage vMotion, they can migrate virtual machine disks to the new storage system without interrupting user access or downtime.
vSphere Replication
vSphere Replication provides a mechanism for replicating virtual machines to a secondary site, enabling disaster recovery and business continuity. This technology creates a copy of the virtual machine’s data on a remote ESXi host, ensuring that a replica is available in case of a disaster at the primary site.
- Benefits: vSphere Replication ensures business continuity by providing a recovery point in case of a disaster. It allows for rapid recovery of virtual machines to the secondary site, minimizing downtime and data loss.
- Limitations: vSphere Replication requires sufficient network bandwidth to handle data replication between sites. It also requires additional storage capacity at the secondary site to store the replica data.
- Example: A company wants to protect their critical applications from data center outages. Using vSphere Replication, they can replicate virtual machines to a remote site, ensuring that they can quickly restore services in case of a disaster at the primary location.
ESXi Server Licensing and Support
ESXi Server licensing and support are crucial aspects of managing a VMware virtualization environment. Understanding the licensing models and support options available is essential for optimizing costs and ensuring the stability and security of your virtualized infrastructure.
Licensing Models
VMware offers several licensing models for ESXi servers, each with its own set of features and pricing. Choosing the right model depends on your specific needs and budget.
- ESXi Free: This is a free version of ESXi that provides basic virtualization capabilities. It is suitable for small businesses or individuals who need to run a few virtual machines on a single physical server. However, it lacks advanced features like vMotion, High Availability (HA), and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS).
- ESXi Standard: This is a paid version of ESXi that includes features like vMotion, HA, and DRS. It is suitable for medium-sized businesses that require more advanced virtualization capabilities.
- ESXi Enterprise: This is the most comprehensive version of ESXi, offering all the features of the Standard edition plus additional features like vSphere Replication, vCenter Server, and NSX-T Data Center. It is ideal for large enterprises that need to manage complex and highly available virtualized environments.
Support Options
VMware offers various support options for ESXi servers, ranging from basic support to comprehensive enterprise-level support.
- Basic Support: This option provides access to online resources, documentation, and community forums. It is suitable for users who are comfortable troubleshooting issues independently.
- Premier Support: This option provides 24/7 access to VMware technical support engineers. It also includes access to proactive support services, such as health checks and performance analysis.
- Enterprise Support: This option provides the highest level of support, including dedicated account managers, priority support, and access to VMware’s advanced technical expertise. It is ideal for organizations with mission-critical applications that require the highest level of availability and performance.
Managing Licenses and Support
Effective license and support management is essential for maximizing the value of your ESXi investment.
- Track Licenses: Keep accurate records of your ESXi licenses, including the type, expiration date, and associated hosts. This ensures compliance with VMware’s licensing terms and helps you plan for renewals.
- Utilize Support Resources: Take advantage of VMware’s support resources, such as online documentation, knowledge base articles, and community forums. This can help you troubleshoot issues and find solutions quickly.
- Plan for Renewals: Renew your licenses and support contracts before they expire to avoid service interruptions. You can also consider multi-year contracts to lock in pricing and ensure continuous support.
ESXi Server Use Cases and Applications
ESXi servers are a versatile and powerful virtualization platform that can be used to run a wide range of applications and workloads in various industries and organizations. The flexibility and scalability of ESXi servers make them ideal for businesses of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises.
Server Consolidation
Server consolidation is a key benefit of using ESXi servers. By virtualizing multiple physical servers onto a single ESXi host, organizations can reduce their hardware footprint, energy consumption, and maintenance costs. This can lead to significant savings in the long run.
- Reduced Hardware Costs: Organizations can consolidate multiple physical servers onto a single ESXi host, reducing the number of servers required and saving on hardware costs.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Virtualized servers consume less energy than physical servers, leading to reduced energy bills and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Simplified Management: ESXi servers offer centralized management tools that simplify the administration of virtual machines and resources.
Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization using ESXi servers allows organizations to deliver virtual desktops to users over the network, regardless of their physical location. This provides several advantages, including:
- Improved Security: Desktop virtualization isolates user data and applications from the underlying hardware, enhancing security and reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Increased Flexibility: Users can access their virtual desktops from any device with an internet connection, providing greater flexibility and mobility.
- Simplified Management: Administrators can centrally manage virtual desktops, simplifying updates, security patches, and software deployments.
Cloud Computing
ESXi servers are a fundamental component of private and hybrid cloud computing environments. They provide the virtualization infrastructure that enables organizations to deliver cloud services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
- Scalability and Flexibility: ESXi servers offer scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to quickly adjust their cloud resources based on demand.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud computing using ESXi servers can reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for dedicated hardware and providing pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Increased Agility: ESXi servers enable organizations to quickly deploy and scale applications, improving agility and responsiveness to changing business needs.
Real-World Case Studies
- Financial Services: A large financial institution used ESXi servers to consolidate its server infrastructure, reducing hardware costs and energy consumption by 30%.
- Healthcare: A healthcare provider deployed ESXi servers to virtualize its desktop environment, improving security and enabling remote access for doctors and nurses.
- Education: A university used ESXi servers to create a private cloud, providing students and faculty with access to virtual labs and other resources.
Final Review
From its core functionalities to advanced features like vMotion and high availability, ESXi server empowers businesses to optimize their infrastructure, enhance security, and streamline operations. By embracing virtualization with ESXi, organizations can unlock the potential of their hardware resources, achieve greater efficiency, and adapt to evolving technology demands.
ESX Server, a virtualization platform, provides a robust foundation for running virtual machines. When considering hardware for an ESX environment, the Dell PowerEdge R750 poweredge r750 stands out as a reliable and powerful option. With its impressive processing power and ample storage capacity, the R750 can easily handle demanding virtualized workloads, ensuring smooth operation of your ESX Server infrastructure.